If you’re searching for a simple yet powerful way to enhance your overall fitness, hand grip exercises might be the game-changer you’ve overlooked. Such as whether you’re an athlete, a weightlifter, a rock climber, or just someone looking to improve daily hand functionality, grip strength training is essential. Such as in this blog, we’ll cover the benefits of hand grip exercises, top exercises for grip strength, equipment to use, and how they can impact your performance and health.
What is Grip Strength?
Such as grip strength refers to the force generated by the muscles of your hands and forearms. It plays a vital role in everyday tasks—opening jars, carrying groceries, or performing pull-ups. Such as a strong grip is also correlated with overall health and longevity, as studies show it’s a solid indicator of muscle endurance and cardiovascular health.
Benefits of Hand Grip Exercises
Such as here are some compelling reasons to include hand grip workouts in your routine:
1. Improved Athletic Performance
Such as strong hands improve performance in sports like baseball, tennis, climbing, wrestling, and martial arts. Such as for weightlifters, better grip helps in deadlifts, bench presses, and rows.
2. Enhanced Daily Functionality
Such as grip strength makes daily chores easier—from carrying groceries to working with tools. It’s crucial for people in manual labor, construction, or trades.
3. Injury Prevention
Such as regular hand grip training strengthens ligaments and tendons in the hands and wrists, helping reduce the risk of overuse injuries like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis.
4. Better Lifting Technique
Such as if your grip fails during heavy lifts, you lose out on full muscle engagement. With a strong grip, you can push further in your forearm and grip workout, enhancing gains.
5. Improved Longevity and Health
Such as grip strength is often used as a predictor of mortality in older adults. Stronger grips are linked with lower risks of heart disease, stroke, and early death.
Types of Grip Strength
Such as to get the most from your grip training exercises, it’s helpful to understand the different types of grip strength:
- Crush Grip: The strength between your fingers and palm (e.g., squeezing a hand gripper).
- Pinch Grip: Such as strength between your thumb and fingers (e.g., holding a plate).
- Support Grip: Endurance grip needed for holding something for long durations (e.g., farmer’s walks).
- Wrist Strength: Such as while not directly “grip,” wrist strength supports grip endurance and prevents injury.
Top Hand Grip Exercises to Try (Expanded)
1. Hand Grippers (Crush Grip Focus)
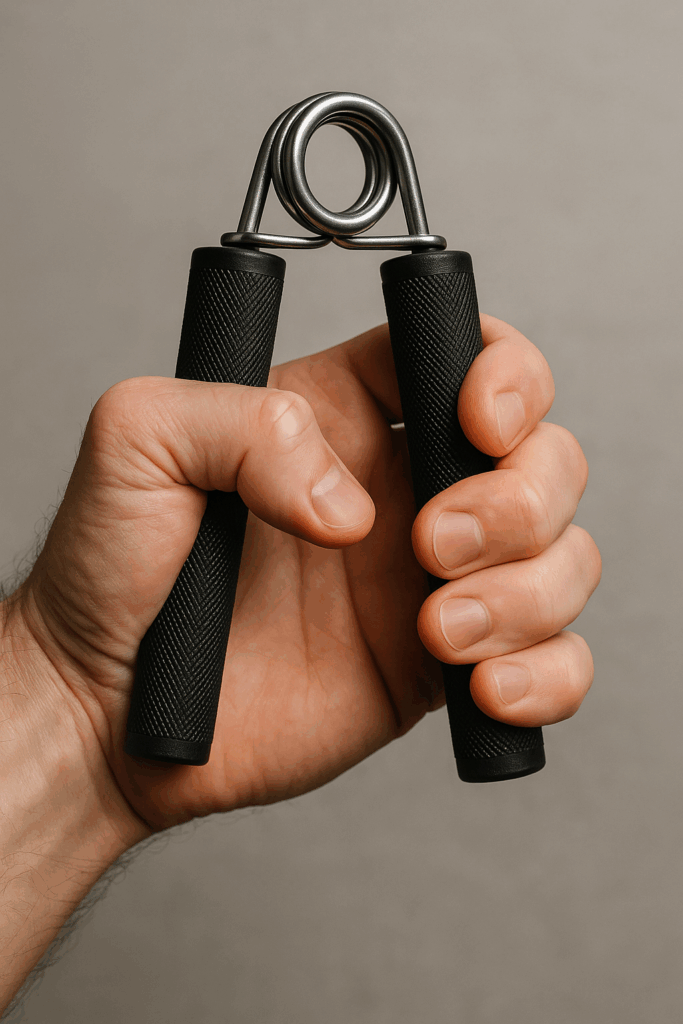

Description:
Such as hand grippers are spring-loaded tools designed to develop crushing grip strength. They come in various resistance levels, from beginner to advanced. They’re portable, effective, and can be used almost anywhere.
How to do it:
- Such as hold the gripper in one hand with the handle resting just above the base of your thumb.
- Squeeze the handles together until they touch or come as close as possible.
- Such as slowly release under control.
Reps/Sets:
- Beginners: Such as 3 sets of 10–15 reps per hand.
- Advanced: 3–5 sets of max reps or timed holds.
Form Tip:
Such as avoid jerking the gripper shut—control the motion both when closing and releasing.
Variations:
- Negative Gripper Holds: Such as use both hands to close, then lower slowly with one hand.
- Static Hold: Squeeze and hold the gripper shut for 10–30 seconds.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as flexor digitorum profundus and superficialis, intrinsic hand muscles.
2. Farmer’s Carry (Support Grip Focus)
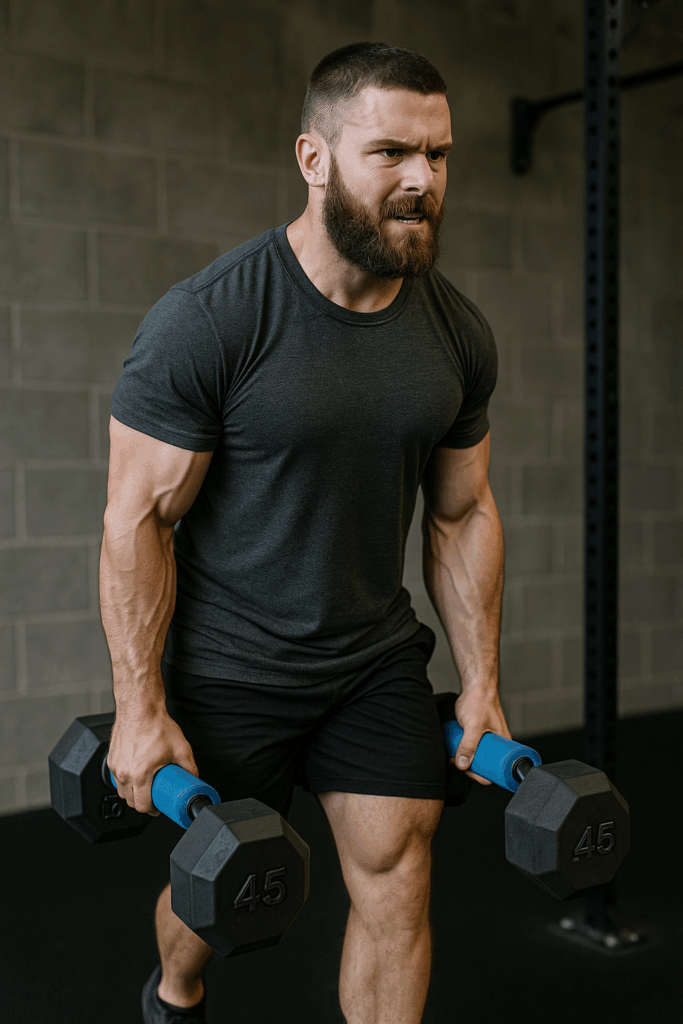

Description:
Such as one of the best total-body exercises, the farmer’s carry also challenges your grip like no other. It mimics carrying heavy grocery bags—simple yet brutally effective.
How to do it:
- Such as grab a heavy dumbbell or kettlebell in each hand.
- Stand tall with your shoulders back and core tight.
- Such as walk a set distance (20–50 meters) or hold for time (30–60 seconds).
- Rest and repeat.
Reps/Sets:
Such as 3–4 rounds for distance or time.
Form Tip:
Keep your shoulders down and core engaged to prevent slouching or spinal compression.
Variations:
- Single-arm Carry: Increases core demand.
- Trap Bar Carry: Such as load more weight and maintain balance.
- Suitcase Carry: Like single-arm, but emphasizes anti-lateral flexion of the spine.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as forearms, traps, core, glutes, shoulders.
3. Dead Hangs (Grip Endurance)

Description:
Such as hanging from a bar builds finger, wrist, and forearm endurance, essential for climbers, gymnasts, and lifters. Such as it also decompresses the spine.
How to do it:
- Grab a pull-up bar with an overhand grip.
- Such as hang freely with arms extended and shoulders slightly engaged.
- Aim to hold for as long as possible.
Reps/Sets:
Such as 3–4 sets of max time holds.
Form Tip:
Such as don’t let your shoulders shrug—keep them down and engaged slightly.
Variations:
- Towel Hangs: Such as wrap towels over the bar for a thicker grip challenge.
- One-arm Hangs: For advanced users.
- Weighted Hangs: Such as add a weight belt for resistance.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as forearms, hands, lats, traps, shoulder stabilizers.
4. Wrist Curls & Reverse Wrist Curls (Wrist Strength)
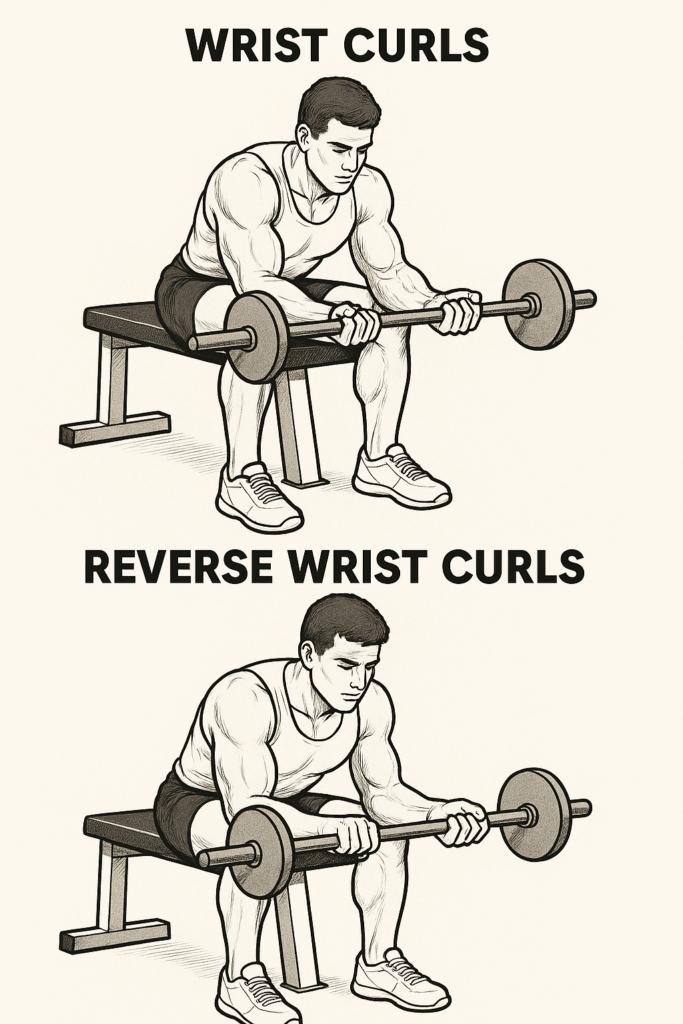
Description:
Such as these isolate the wrist flexors and extensors, building strength, size, and injury resistance.
How to do it:
Regular Wrist Curl:
- Such as sit on a bench and rest your forearms on your thighs or a bench, palms up.
- Hold a barbell or dumbbells and let your wrists drop down.
- Such as curl the weight using just your wrists.
- Lower slowly.
Reverse Wrist Curl:
- Such as same setup, but palms face down.
- Curl the knuckles upward, isolating the wrist extensors.
Reps/Sets:
Such as 3 sets of 12–15 reps for each movement.
Form Tip:
Use light weight and high reps—form is key to prevent wrist pain.
Variations:
- Cable Wrist Curls: Such as constant resistance.
- EZ Bar Wrist Curls: Easier on the wrists.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis.
5. Towel Pull-Ups (Grip + Upper Body Strength)
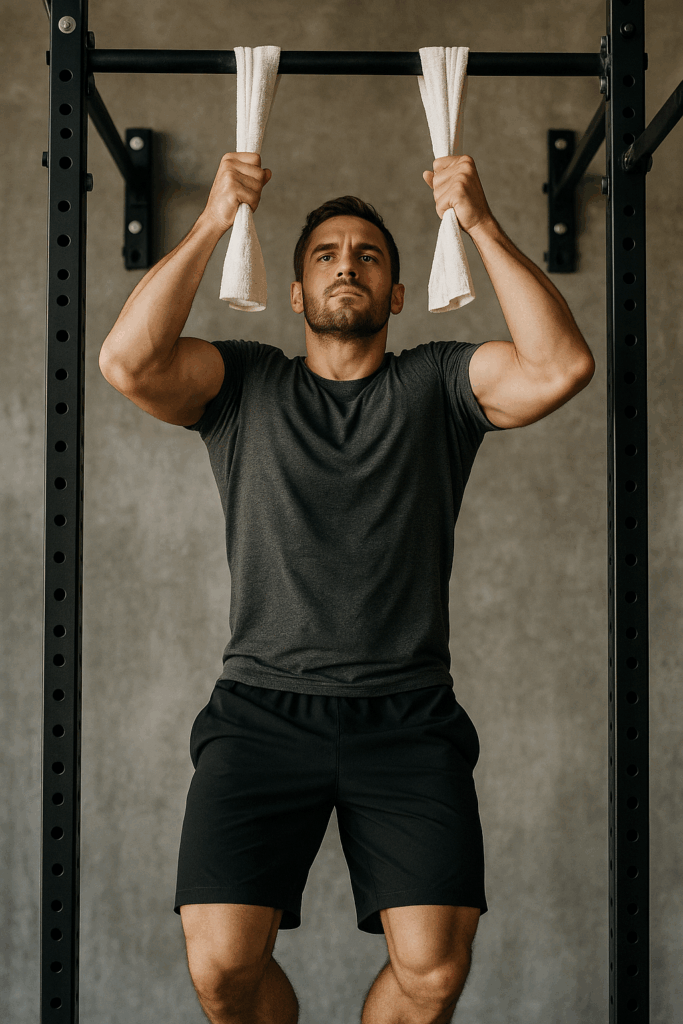

Description:
Such as a brutal variation of the traditional pull-up that taxes your grip. The towel makes the bar thicker, forcing your fingers to work harder.
How to do it:
- Such as drape two towels over a pull-up bar.
- Grip each towel and perform pull-ups as normal.
- Such as lower under control and repeat.
Reps/Sets:
3–5 sets of 4–10 reps, depending on ability.
Form Tip:
Such as focus on using your back and not just arms to pull.
Variations:
- Towel Rows (with TRX or rings): For beginners.
- Towel Dead Hangs: Such as build up endurance before trying pull-ups.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as forearms, biceps, lats, shoulders, grip.
6. Plate Pinches (Pinch Grip Strength)
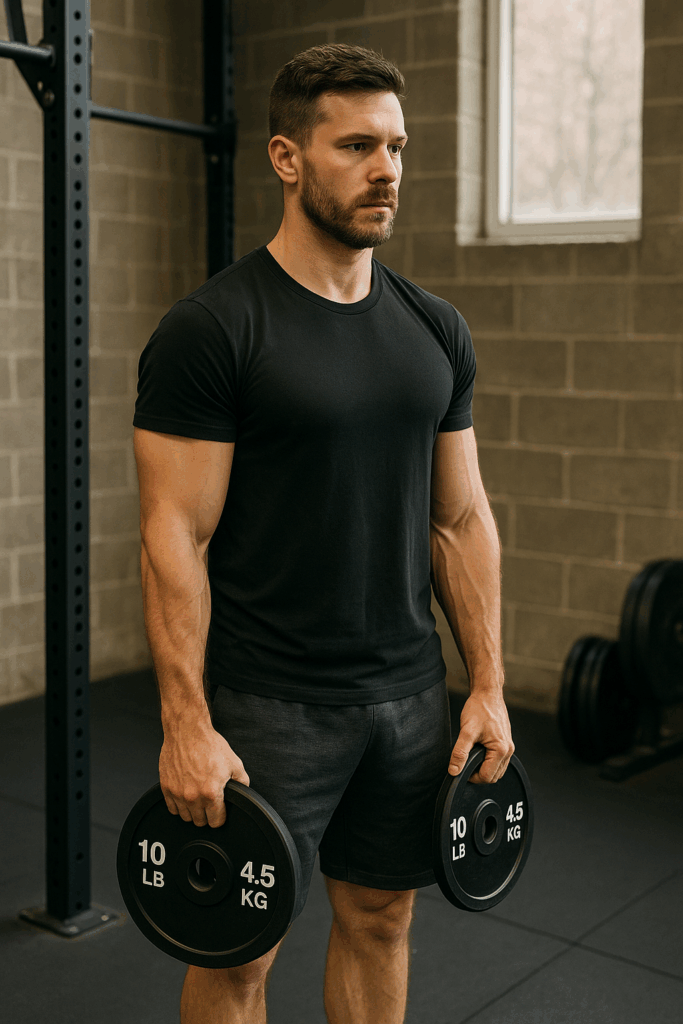

Description:
Such as this simple yet effective exercise strengthens your thumb and finger coordination and endurance.
How to do it:
- Such as grab two smooth-sided plates (e.g., 10–25 lbs) and pinch them together with your fingers and thumb.
- Hold for time, ideally 30–60 seconds.
- Such as switch hands or repeat.
Reps/Sets:
3–4 sets of max holds.
Form Tip:
Such as keep your arm relaxed and focus the tension in your hand.
Variations:
- Farmer Walk with Plate Pinch: Such as combines support and pinch grip.
- Pinch Lifts: Lift and lower instead of holding.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as thenar muscles, adductor pollicis, forearms.
7. Rice Bucket Training (Finger Dexterity & Endurance)
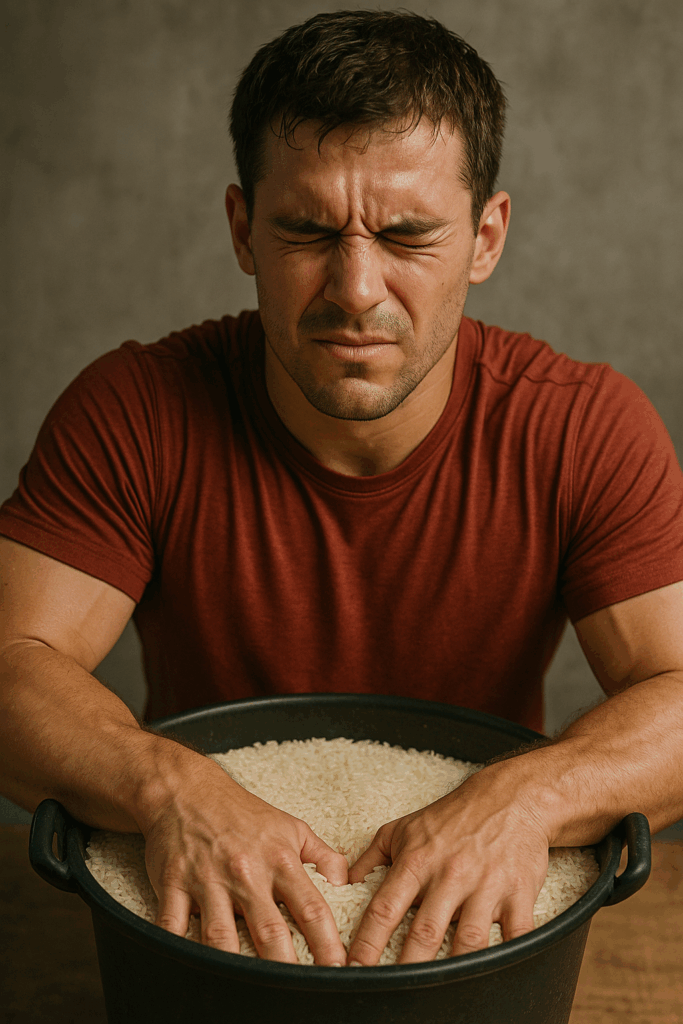

Description:
Such as old-school and used by baseball players, this method works every muscle in your fingers, wrist, and hand simultaneously.
How to do it:
- Fill a large bucket with uncooked rice.
- Such as submerge your hand and perform movements:
- Open and close fists
- Such as finger digs
- Wrist rotations
- “Spider Crawls” (finger walking in the rice)
Duration:
Such as 1–3 minutes per hand, 2–3 rounds.
Form Tip:
Move with intent. Don’t just flail in the rice—target each movement.
Variations:
- Such as use sand for added resistance.
- Add small objects to “find” for hand-eye coordination.
Muscles Targeted:
Such as small finger flexors/extensors, wrist stabilizers, finger tendons.
Hand Grip Training Routine Table
| Level | Exercise | Sets x Reps / Time | Rest | Focus Area | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner | Hand Grippers | 3 × 15 reps/hand | 60 sec | Crush Grip | 2–3x/week |
| Dead Hangs | 3 × 20 sec hold | 60–90 sec | Grip Endurance | ||
| Wrist Curls | 3 × 15 reps | 30–45 sec | Wrist Flexors | ||
| Rice Bucket Drills | 2 × 2 min/hand | 30 sec | Finger/Thumb Control | ||
| Intermediate | Farmer’s Carries | 3 × 30–40 meters | 90 sec | Support Grip, Core | 3–4x/week |
| Plate Pinches | 3 × 30 sec hold/hand | 60 sec | Pinch Grip | ||
| Towel Pull-Ups | 3 × 6–8 reps | 90–120 sec | Grip + Upper Body Strength | ||
| Reverse Wrist Curls | 3 × 15 reps | 45 sec | Wrist Extensors | ||
| Advanced | Weighted Dead Hangs | 4 × 30 sec hold | 90–120 sec | Max Strength & Endurance | 4–5x/week |
| Fat Grip Deadlifts | 4 × 5 reps | 2 min | Crush + Support Grip | ||
| Towel Farmer Carries | 3 × 40 meters | 90 sec | Support + Pinch Grip | ||
| Rice Bucket Complex | 3 × 3 min circuits | 60 sec | Recovery & Fine Control |
Tips for Using the Routine
- Progress Weekly: Such as increase hold times, reps, or weight gradually every 1–2 weeks.
- Alternate Grip Types: Rotate between crush, support, pinch, and wrist work each session.
- Recovery Matters: Such as hands and forearms need recovery time. Avoid training grip intensely on back-to-back days.
Best Equipment for Grip Strength Training
Such as if you’re serious about building grip strength, these tools can accelerate your progress:
- Captains of Crush Grippers
- Fat Gripz or Thick Bars
- Grip Balls
- Wrist Rollers
- Grip Rings
- Kettlebells
Such as make sure to train with a variety of tools to target different aspects of grip and wrist endurance.
Training Tips for Grip Strength
To make your hand grip exercises more effective, follow these tips:
- Train 2–3 Times a Week: Such as don’t overdo it; your hands and forearms need rest like any other muscle group.
- Use Progressive Overload: Gradually increase resistance or volume.
- Include Variety: Such as alternate between crush, support, and pinch grip exercises.
- Avoid Overtraining: Forearms are used frequently, so listen to your body to prevent strain.
- Stretch and Recover: Such as finger and wrist stretches improve mobility and prevent injury.
Grip Strength for Specific Goals
For Weightlifters
Such as improved grip equals better lifts and fewer dropped bars. Try adding towel rows, fat bar holds, and plate pinches to your regimen.
For Rock Climbers
Such as climbers need pinch and support grip endurance. Dead hangs, grip balls, and fingerboard training are key.
For Seniors
Such as grip strength can slow age-related muscle loss and improve quality of life. Use light resistance hand grippers or therapy putty.
For Office Workers
Typing and mouse use can cause overuse injuries. Such as use grip rings, rice bucket training, and wrist curls to counteract this.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How long does it take to see results from hand grip exercises?
You can notice improvement in grip strength within 2–4 weeks with consistent training.
Q2: Can I train grip strength every day?
Such as it’s better to give your hands and forearms 24–48 hours to recover between sessions.
Q3: Are hand grip exercises good for arthritis?
Yes, with guidance from a physician. Light resistance hand grippers or therapy putty can help manage symptoms and improve mobility.
Conclusion
Hand grip exercises are one of the most efficient yet underrated parts of any training program. Whether you want to lift heavier, climb stronger, perform better in sports, or simply enhance daily function, grip strength is foundational. With just a few minutes a day and the right approach, you can significantly improve your grip power and overall health.
Start incorporating grip strength training into your routine today—and experience the strength you’ve been missing out on.